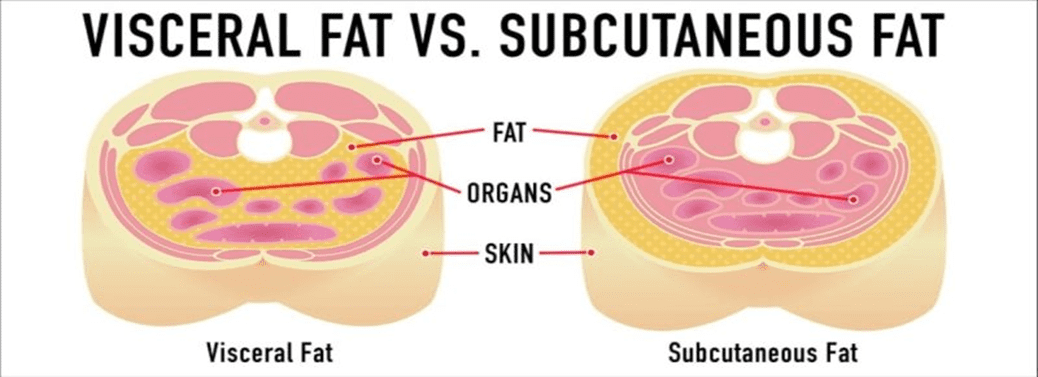
Exercise as Medicine: How Physical Activity Can Prevent (Even Reverse) Heart
From Light Walks to Heavy Weightlifting – How to Defend and Strengthen Your Heart
Why Moving Your Body Is Important to the Heart
By exercising your heart, it will become stronger just like your muscles. However, most people over age 18 are not moving enough to take care of their bones.
Exercise As a Tool Against Cardiovascular Disease.
Clears Clogged Arteries:
- Exercise that requires using oxygen results in HDL cholesterol cleaning the lining of the arteries.
- 150 minutes of brisk walking a week may lower your chances of coronary artery disease by 30%.
Lowers Blood Pressure:
- 7 to 12 points lower systolic BP have been found with strength training, making it almost equivalent to what medications provide.
Prevents Deadly Clots:
- Being active regularly helps blood move, making it less likely you will experience DVT or stroke.
Rebuilds Weak Hearts:
- Patients in cardiac rehab programs who exercise have a higher chance of living longer after a heart attack
Best Exercises for Your Heart, Organized by Special Condition
When this condition occurs, focus on this type of exercise and try to avoid this type
With High Blood Pressure, you should choose swimming, cycling, or yoga instead of heavy weightlifting.
If you have Heart Failure, choose to walk or do seat elliptical workouts.
According to medical experts, too much caffeine should be avoided, and you should do moderate jogging.
After the stent or surgery, patients should do supervised cardiac rehab, and contact sports are not allowed
A good rule is that if you are working out so much that you can talk, but not sing, you are in the heart-healthy zone.

3 Heart-Helping Habits (You Can Do Them at Home)
- The 20-Min Daily Lifesaver:
- 5 min of fast walking is followed by 3 min of speed walking and 2 min of slow walking, which is repeated again.
- It can make heart disease deaths go down by 24%.
- Desk-Job Rescue:
- Set an alarm to go off every hour and do a 60-second wall sit with calf raises
- Let’s you avoid issues related to DVT.
- Bedroom-to-Bathroom Workout (For Weak Hearts):
- Stay where you are and continue your exercises as ads are shown on TV.
- Use stretches such as leg lifts during your regular teeth brushing routine
What to Watch Out for When Things Go Wrong with Exercise
Stop Immediately If You Feel:
- Having discomfort or pain in the chest
- Noticing that you are about to lose your balance quite fast
- It is possible for people to feel their heart racing.
- Regular and serious troubles breathing
Critical Note: Sedentary? It is wise to have a stress test done before you begin intense exercises.
Your Workout Plan for Improving Heart Health
For Prevention:
- 150 minutes a week of light exercise (just like gardening or dancing)
- You should strength train 2 times a week, using weights are okay if you have them; bands or bodyweight are also fine.
CONCLUSION
Exercise is very important when it comes to treating and preventing cardiovascular diseases. Many studies prove that often doing physical activities in a regular way offers significant health benefits.
It helps the heart work better and boosts health in blood vessels, controls important risk factors, helps people manage weight, and improves their sense of well-being. Because it is affordable, reliable, safe with the right dosage, and has few side effects, exercise is a basic and important element of treating heart disease.
Even though individual plans must reflect a person’s health condition and comorbidities, the overall advice is clear: it is key for people with or at risk of heart disease to regularly do moderate aerobic and resistance exercises to boost their health. Sticking to a regular exercise plan gives patients the ability to look after their heart health on their own.