A drowning experience struck me as I remained completely dry on solid ground. I tried to rest before my sudden violent coughing attack because my airflow developed that terrifying bubbling sound and breathing became hard. The effort to breathe became overwhelmingly overwhelming since my lungs burned like open flames. Fear became visible when panic seized control of my mind. Breathing became my sole preoccupation while I battled to take in air at that moment.
The buildup of fluid inside lung alveoli structures blocks gas exchange which creates pulmonary edema. The presence of excessive fluid within lungs creates dangerous medical emergencies that cut off blood oxygen flow and block regular breathing functions.
Heart illnesses typically cause pulmonary edema yet this condition emerges sometimes from non-heart-related origins.
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema (Heart-Related)
- Heart Failure: The most common cause. When the heart becomes weak it fails to properly circulate blood which creates fluid accumulation first in pulmonary veins then in the lungs.
- A heart attack which damages heart muscle tissue reduces cardiovascular function and allows fluid retention.
- Malfunctions in the heart valves prevent regular blood flow which causes enhanced pressure in the pulmonary veins.
- Continuous hypertension causes heart strain which puts people at higher risk for both heart failure and pulmonary edema.
- Heart conditions that affect heart muscle function result in muscle weakness that causes fluid accumulation in the body.
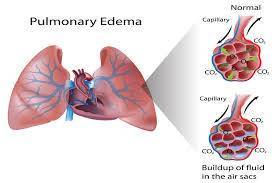
Non-Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema (Non-Heart-Related)
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) develops as a severe lung condition from infections alongside trauma or alternative causes resulting in lung inflammation and fluid leakage.
- At high altitudes low oxygen supply triggers High Altitude Pulmonary Edema (HAPE) by breaking down lung tissues which allows fluid to escape into air spaces.
- Some medications together with excessive drug intake can damage lung tissue which results in fluid accumulation in the lungs.
- Exposure to toxic substances through the lungs leads to inflammation and damage of the respiratory system.
- The process of near drowning results in water ingestion which produces fluid accumulation in the lungs.
- Impaired kidney function brings about fluid overload which leads to pulmonary edema.
Symptoms of Pulmonary Edema
- Breathing difficulties known as dyspnea become worse during physical activity as well as during rest.
- Breathlessness along with coughing produces either frothy sputum or iridescent tinge mucus material which contains blood.
- Airway narrowing produces wheezing or gasping sounds that increase the breathing noise.
- The body increases its breathing rate because oxygen levels become low.
- The symptom combination of chest pain and tightness often appears with other pulmonary edema manifestations.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired.
- Anxiety or restlessness: Due to difficulty breathing.
Due to insufficient oxygen levels the person will display either pale skin or develop bluish skin discoloration (cyanosis).
- The patient might experience heavy sweating along with moist skin.
- Swelling in the legs or feet exists as a symptom when pulmonary edema arises from heart failure.
Diagnosis of Pulmonary Edema
- The evaluation of pulmonary sounds with a stethoscope enables healthcare providers to detect fluid through examination of crackling lung noises (rales).
- The Chest X-ray gives doctors visibility into lung fluids while showing heart dimensions.
- Blood tests provide data about combined oxygen levels together with assessment of kidney functions and other diagnostic markers.
- A heart ultrasound known as echocardiogram evaluates heart structure alongside its functional activity.
- Medical personnel use additional tests like electrocardiograms (ECGs) to issue assessments about heart rhythm when required.
Treatment of Pulmonary Edema
- Treatment of pulmonary edema needs immediate medical intervention because it creates an urgent situation that requires better oxygenation and breathing functionality.
- Extra oxygen becomes a part of the treatment as health professionals provide supplemental oxygen to enhance blood oxygen levels.
Medications:
- Both diuretics and other fluid-removal medications exist for body fluid reduction purposes.
- Vasodilators serve as medical agents that make blood vessels more relaxed therefore lowering lung pressure.
- The required medications may include alternate treatments based on specific prescription requirements for heart function enhancement or infectious treatment.
- A breathing machine termed mechanical ventilation assists breathing when patients experience severe conditions.
- Treatment of Underlying Cause: Addressing the root cause of pulmonary edema, such as heart failure, infection, or drug reaction.
Complications of Pulmonary Edema
- Douglas Payne notes that death occurs because oxygen deprivation proceeds to cause respiratory failure before damaging organs until the body shuts down.
- Heart attack which damages cardiovascular system functions represents a possible result once pulmonary edema develops.
- Lungs with fluid pose higher risk for pneumonia development.
- Prolonged severe cases of pulmonary edema produce enduring damage to the lung tissue structure.
Prevention of Pulmonary Edema
- People with heart conditions should keep their heart failure and hypertension under control as well as their related heart problems.
- The defense against pulmonary edema begins through life choices which combine nutritious food consumption with physical activity as well as abstaining from smoking.
- Check for hazardous substances that enter your respiratory system.
- After climbing to high elevation regions people need to adopt a slow ascent to enable their body to adjust to the local environmental conditions.
Conclusion
- Medical professionals must immediately provide proper treatment for patients suffering from pulmonary edema. Patients will enhance their recovery potential through early medical intervention when they possess both symptom recognition and disease cause understanding. You should seek prompt medical evaluation through healthcare providers or emergency services for any changes in your breathing or appearance of alarming new symptoms.