A quick obstruction works quietly to threaten your lung tissues through the medical condition called pulmonary embolism. Numerous individuals experience the medical crisis called pulmonary embolism (PE) without being aware of it during yearly occurrences. Are you at risk? Understand all warning indicators and available safety practices to resist health risks.
Risks to check for pulmonary embolism (PE) include blood clots that separate from veins primarily in the lower legs and move to obstruct lung blood vessels.
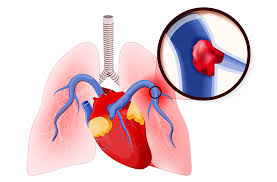
Pulmonary Embolism
Symptoms of Pulmonary embolism (PE)
Pulmonary embolism symptoms exist on two levels with distinct clear indicators yet other nonspecific signs depend on the clot size combined with lung tissue damage extent. Unbeknownst to many people with PE the condition produces no clear signs or their symptoms remain minimal. Common symptoms of a PE include:
- Shortness of breath
- The symptoms of pulmonary embolism include breast pain that appears when someone coughs or takes a deep breath.
• Rapid breathing
• Rapid heart rate
• Coughing up blood
• Lightheadedness or fainting
The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism requires examination through patient history combined with physical assessment and medical tests. The following are some widespread evaluation procedures.
Blood tests:
Medical professionals use D-dimer blood tests to determine protein breakdown products occurring in your body. Patients with pulmonary embolism have elevated D-dimer protein levels in their blood but this pattern overlaps with several medical issues that result from widespread blood coagulation.
(CBC) complete blood count will help identify alternative infections or conditions producing your current symptoms such as anemia.
Imaging tests:
Chest X-ray:
The chest X-ray does not detect pulmonary embolism yet it provides a diagnosis ruling out alternative conditions and detects pulmonary hypertension when other tests yield negative results.
Computed tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA):
Pulmonary embolism detection relies on the specific test since it remains the most effective diagnostic procedure for patients. The procedure utilizes a single CT scan to reveal blocked lung blood vessels while viewing lung blood vessel imaging through contrast dye administration.
Ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) scan:
The test tracks blood flow in your arm veins and tracks radioactive gas uptake during breathing to evaluate lung health by measuring blood movement and air activity. Medical experts can identify pulmonary embolisms through findings beyond standard examination results.
Echocardiogram:
A heart ultrasound scan displays the extent of pulmonary embolism damage while revealing how much organs in the heart can tolerate.
Other tests:
The Electrocardiogram (ECG) records standard heart electricity patterns while identifying irregular heart rhythms that signal pulmonary embolism.
An ultrasound device emits sound waves to identify deep vein clots in the legs which represent the primary source of pulmonary embolisms.
The duration of recovery depends on various factors.
- Giant blood clots and excessively large vessels generate elongated healing times because of their destructive properties.
- Patients who have serious pulmonary embolisms need longer recovery times when their symptoms persist before reaching full health recovery.
- Patients with different overall health conditions may face either shortened or extended healing times for pulmonary embolism.
These specific guidelines will assist patients during their Pulmonary embolism (PE)
healing process:
- Doctors will prescribe particular treatment plans that might necessitate patients to take blood thinners and perform physical therapy while making necessary changes to their daily routine.
- Through physical exercise individuals develop better blood flow while improving their heart health.
- Body recovery flows better as symptoms stay stable when you maintain a well-balanced eating regimen.
Conclusion
The outcomes in pulmonary embolism become more beneficial through proper awareness and timely diagnosis combined with immediate medical intervention. Consult your doctor regarding your risks and get prompt medical help if you notice any associated signs. Your health is paramount.

